Mon - Fri: 9 am - 5 pm
Online store always open
Mon - Fri: 9 am - 5 pm
Online store always open
GET CERTIFIED @ ONE OF OUR CONVENIENT TRAINING SITES!
[PITTSBURGH-LAWRENCEVILLE & CRANBERRY TOWNSHIP LOCATIONS]
NEED AN ONSITE CLASS AT YOUR LOCATION? CLICK HERE.
Western Pennsylvania and Pittsburgh Leader in CPR Classes | Master Zoll AED Distributor

Many people think heart attacks and sudden cardiac arrest are the same thing, but they are actually different. Understanding these differences can help save lives. A heart attack happens when blood flow to a part of the heart is blocked. This can seriously damage the heart muscle. Sudden cardiac arrest, on the other hand, happens when the heart suddenly stops beating. This is usually due to a problem with the heart’s electrical system.
This article will clarify what heart attacks and sudden cardiac arrest are. It will help you learn the key differences between the two and what needs to be done in each situation. With this knowledge, you can be better prepared to help someone in a medical emergency.
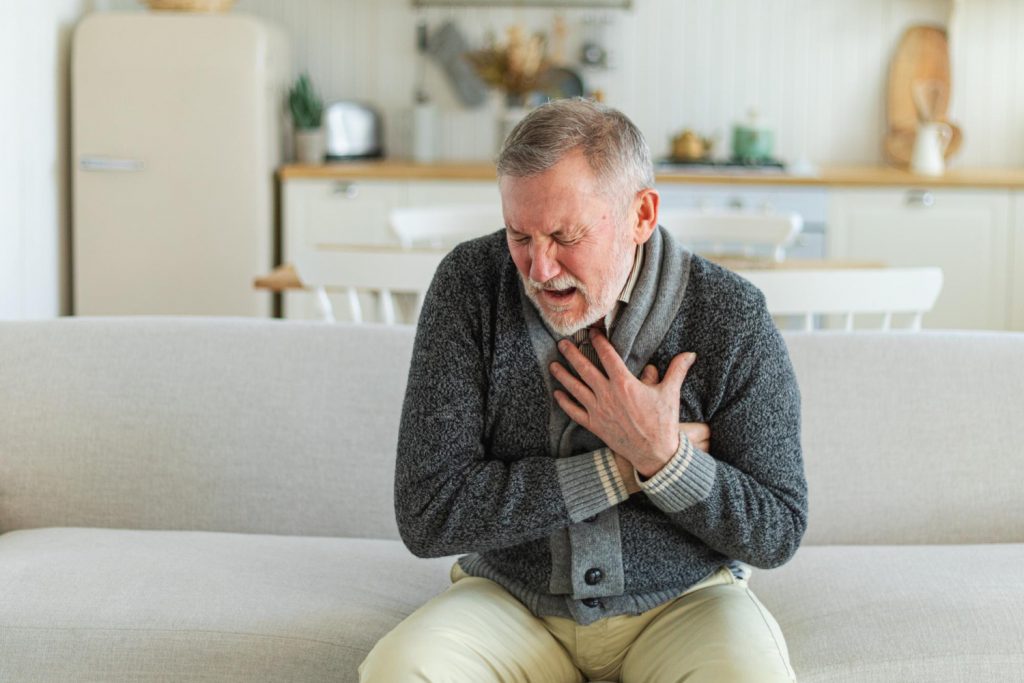
A heart attack occurs when blood flow to part of the heart is blocked, often by a blood clot. This blockage keeps oxygen from reaching the heart muscle, causing that part of the heart to get damaged or die. The main cause is usually a buildup of fat, cholesterol, and other substances, which form a plaque in the heart arteries. When this plaque breaks away, it can form a clot that blocks blood flow.
Symptoms of a heart attack can vary, but some common warning signs include:
1. Chest Pain: Most people feel discomfort or pain in their chest. This can feel like pressure, tightness, or squeezing.
2. Upper Body Pain: Pain can spread to arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach.
3. Shortness of Breath: This may occur with or without chest discomfort.
4. Other Signs: Cold sweat, nausea, or lightheadedness.
Sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) happens when the heart suddenly stops beating. This is usually due to an electrical problem that causes the heart to beat irregularly. When this happens, blood stops flowing to the brain and other vital organs. SCA is a medical emergency that needs rapid treatment.
The causes of sudden cardiac arrest include:
1. Heart Conditions: Prior heart attacks, coronary artery disease, or heart failure.
2. Electrical Disorders: Problems with the heart’s electrical system, like arrhythmias.
3. Other Factors: Severe physical stress, low blood levels of potassium or magnesium, and genetic disorders.
Although heart attacks and sudden cardiac arrest can both be scary, they are different in many ways. A heart attack is caused by a blockage in the arteries that reduces blood flow to the heart muscle. Sudden cardiac arrest results from an electrical issue in the heart that causes it to stop beating.
Comparing the symptoms can help clarify these differences. Heart attack symptoms usually include chest pain, discomfort in the upper body, shortness of breath, and other signs like nausea or cold sweat. These symptoms can develop slowly or suddenly and might vary in intensity. Sudden cardiac arrest, on the other hand, has more immediate and severe symptoms such as sudden collapse, no pulse, no breathing, and loss of consciousness.
Understanding the difference between a heart attack and sudden cardiac arrest is crucial. Heart attacks are caused by blocked blood flow to the heart muscle, while sudden cardiac arrest happens when the heart’s electrical system fails. Knowing the symptoms of each condition and how to respond can save lives.
By recognizing these conditions and knowing the right steps to take, you can be prepared to help in an emergency. For top-quality First Aid and CPR training, AED distribution, and program management solutions, trust Square One Medical to guide you. Learn more about our services and how you can be prepared to save lives at www.sq1med.com.